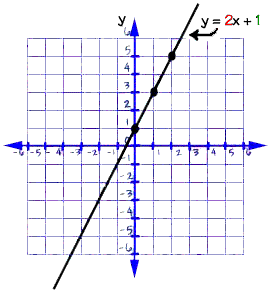
Every straight
line can be represented by an equation: y = mx + b. The coordinates of every
point on the line will solve the equation if you substitute them in the equation
for x and y.
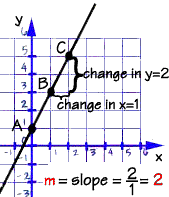
The slope
m of this line - its steepness, or slant - can be calculated like this:
m = change in y-value
change
in x-value
The
equation of any straight line, called a linear
equation, can be written as: y = mx + b, where m
is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept. 
The
y-intercept
of this line is the value of y at the point where the line crosses the y axis.



![]()
![]()